Why is My Furnace Blowing Cold Air?
When winter hits, a warm and cozy home is essential for comfort and safety. However, if your furnace starts blowing cold air, it can quickly become a cause for concern. There are several common issues that can lead to a furnace blowing cold air, and in this comprehensive guide, we will cover these issues and provide troubleshooting tips and DIY solutions to help you restore warmth to your home.
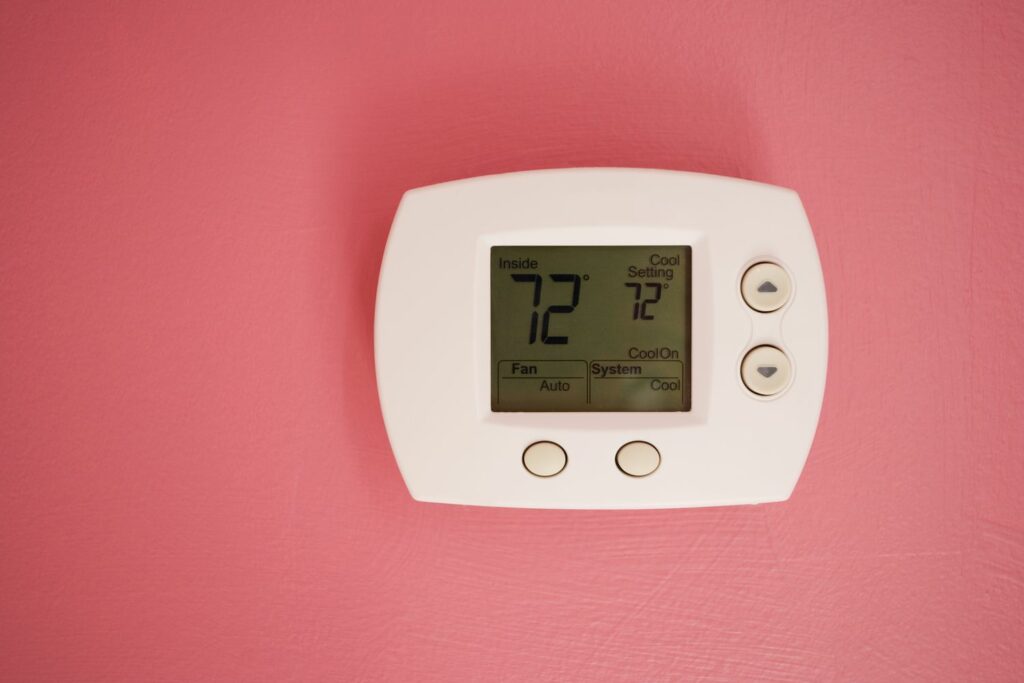
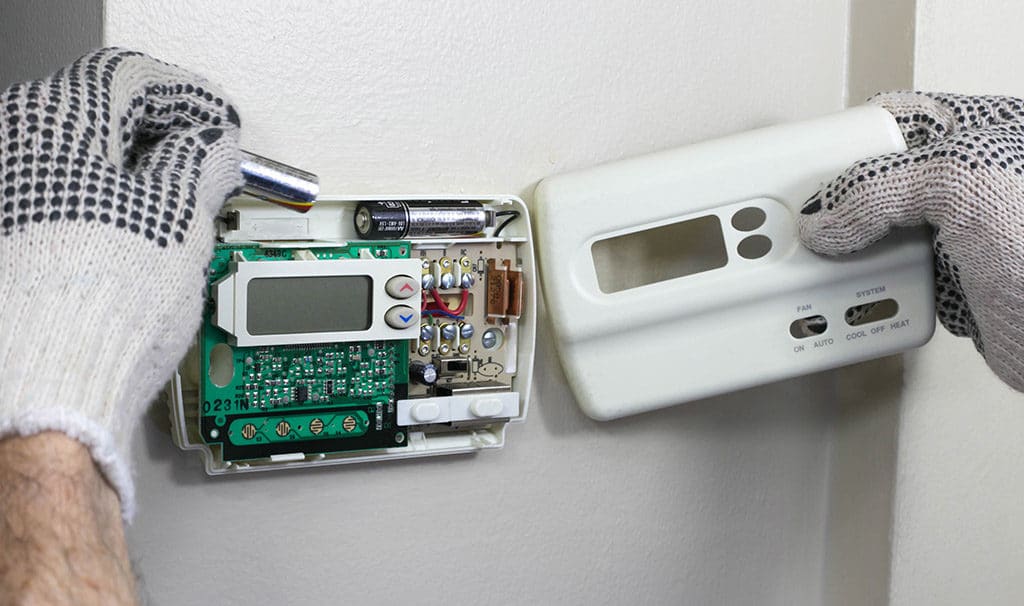
1. Thermostat Settings and Issues
Incorrect Fan Settings
The first and easiest thing to check when your furnace is blowing cold air is the thermostat fan setting. Make sure the fan is set to ‘Auto’ and not ‘On.’ If the fan is set to ‘On,’ it will continuously blow air, whether the furnace is producing heat or not. This can result in a mixture of hot and cold air blowing from your vents.
Thermostat Malfunction
If your thermostat settings are correct, but your furnace continues to blow cold air, it could be a sign of a malfunctioning thermostat. In this case, you may need to replace the thermostat or call a professional HVAC technician to diagnose and fix the issue.
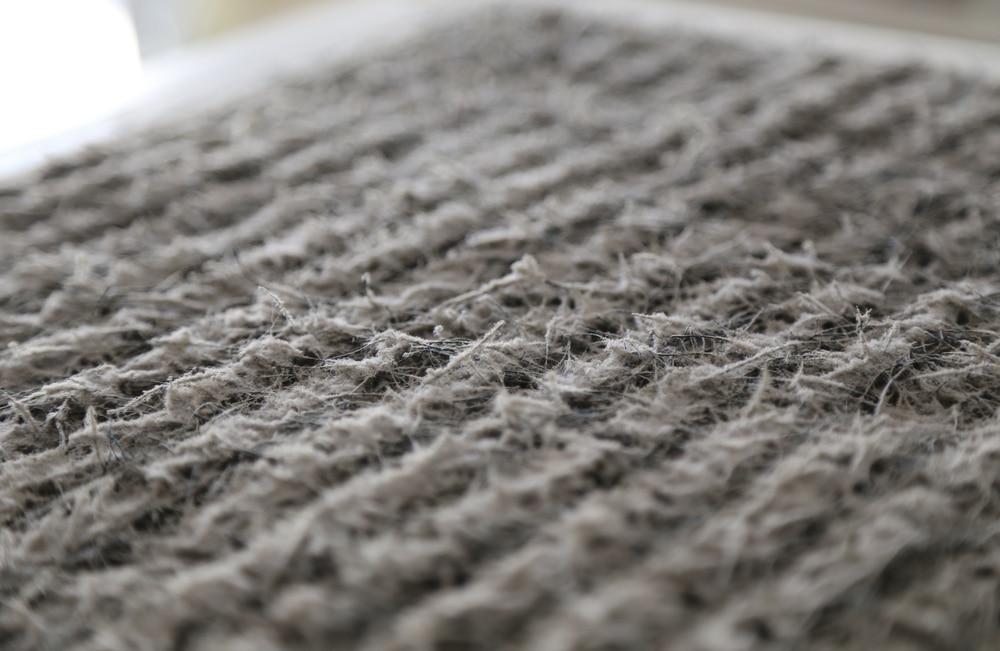
2. Dirty or Clogged Air Filter
A dirty or clogged air filter can restrict airflow to the furnace, causing it to overheat and shut down as a safety precaution. When this happens, your furnace may blow cold air temporarily before shutting off completely. To resolve this issue, inspect your air filter to see if it needs to be replaced. Make sure to change your air filter regularly, at least every 90 days, to prevent this issue from recurring.
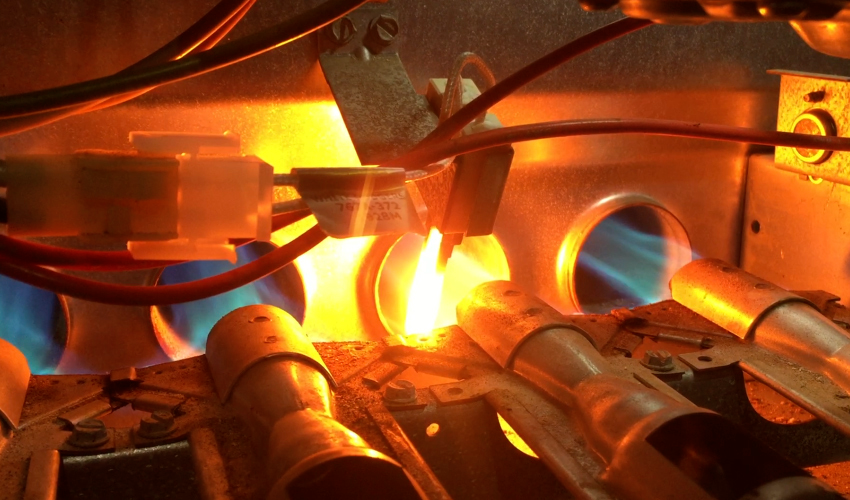
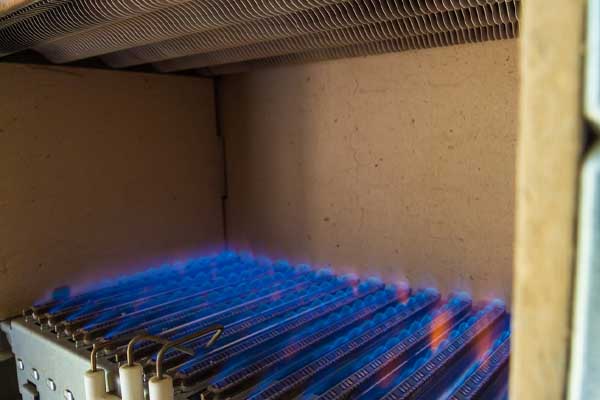
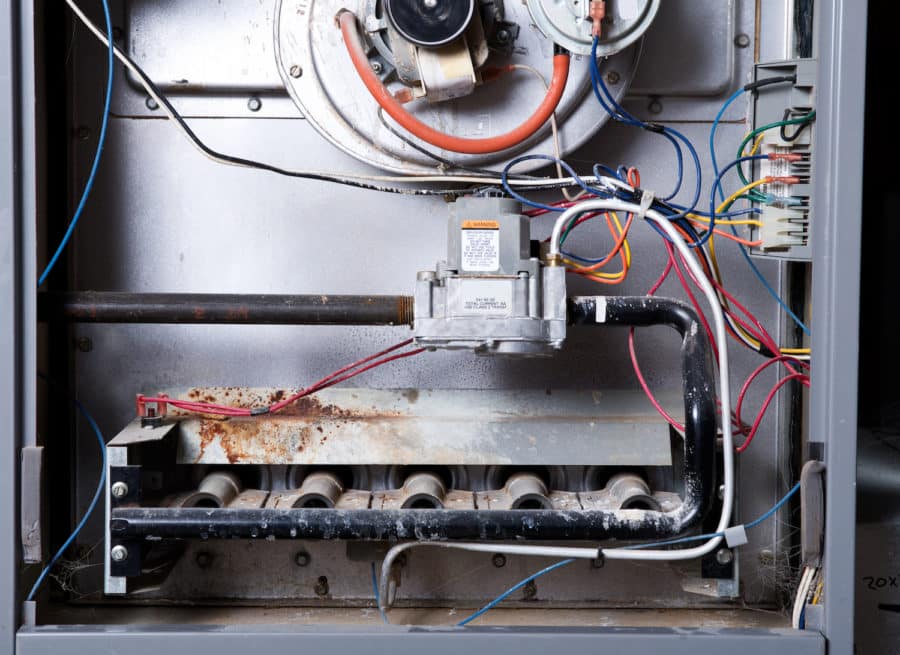
3. Pilot Light or Igniter Issues
Pilot Light Problems
Gas furnaces rely on a pilot light or an igniter to ignite the natural gas and produce heat. If the pilot light goes out or the igniter fails, the furnace will not produce heat and will instead circulate cold air. To fix this issue, you can attempt to relight the pilot light by following the instructions on your furnace. If the pilot light keeps going out or won’t relight, it may need cleaning or professional attention.
Igniter Issues
Modern furnaces typically use an electronic igniter instead of a pilot light. If your furnace has a faulty igniter, it will need to be replaced. This is a more complex repair that may require the assistance of a professional HVAC technician.
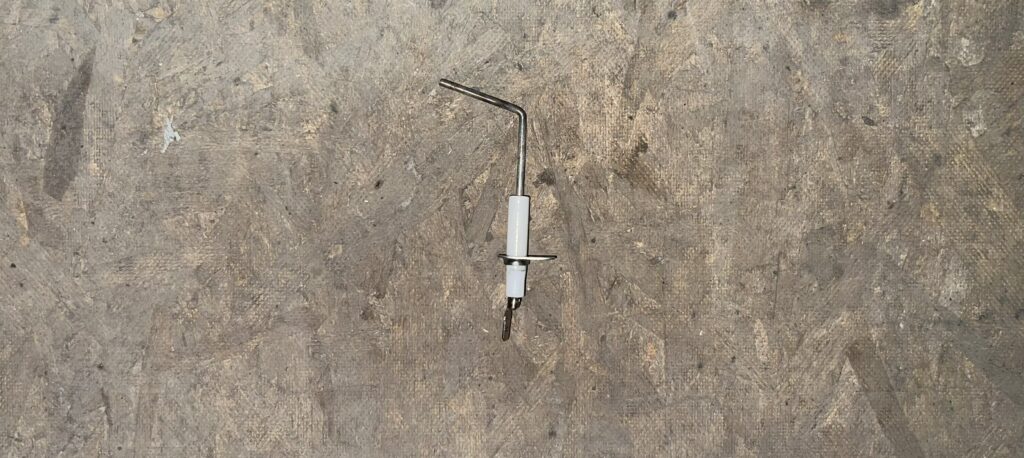
4. Dirty Flame Sensor
A dirty flame sensor can cause your gas furnace to blow cold air and then shut off abruptly. The flame sensor is a safety feature that detects heat from the furnace flame. If the sensor becomes dirty or covered in debris, it may not detect the heat and will shut down the furnace to prevent a potential gas leak. To fix this issue, turn off the power to the furnace, remove the flame sensor, and clean it with an emery cloth or fine steel wool. Once cleaned, reinstall the sensor and turn the power back on.
5. Overheating Furnace
An overheating furnace can cause it to blow cold air and then shut down as a safety precaution. There are several reasons why a furnace may overheat, including dirt buildup, mechanical failure, and old age.
Dirt Buildup
If your air filter is clogged or the furnace itself is dirty, it can cause restricted airflow and lead to overheating. In this case, clean or replace your air filter and schedule a professional furnace cleaning to resolve the issue.
Mechanical Failure
Wear and tear on your furnace can lead to mechanical failure and overheating. If you suspect a mechanical issue, it’s best to call a professional HVAC technician to diagnose and repair the problem.
Old Age
As furnaces age, their performance declines, and they can become more prone to overheating. If your furnace is nearing the end of its lifespan (typically around 15 years), it may be time to consider a replacement.
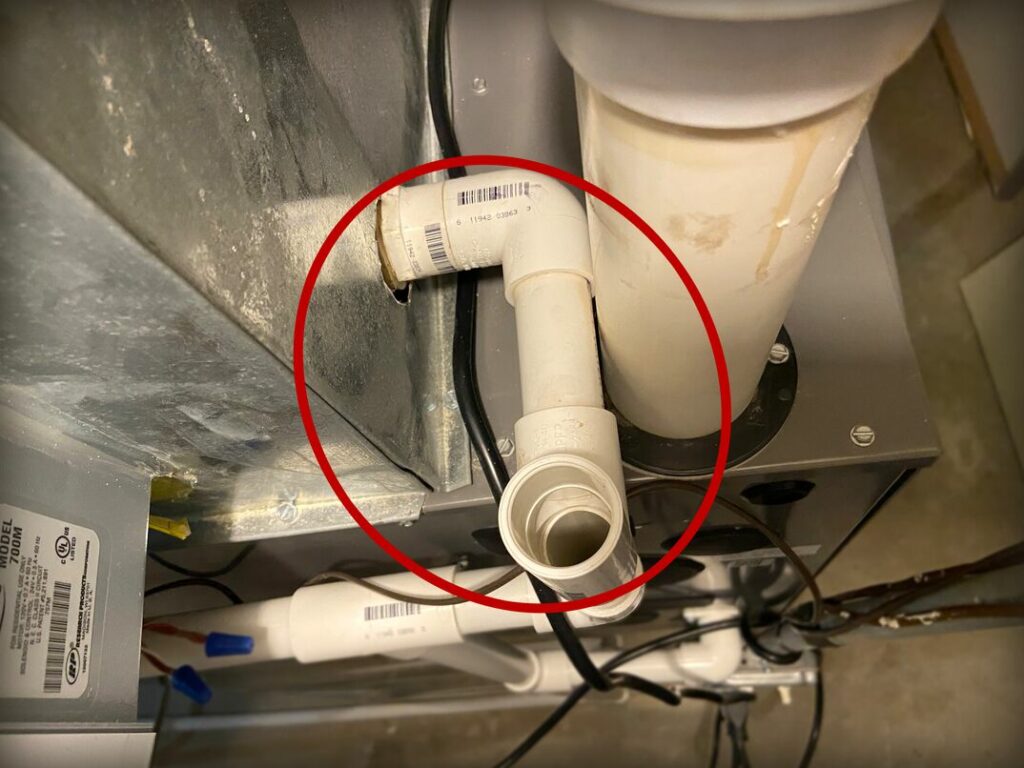
6. Clogged Condensate Line
High-efficiency gas furnaces and those connected to a central AC system have condensate lines that allow excess water to drain away from the unit. If the condensate line becomes clogged with dirt or debris, water may back up, triggering a safety shut-off switch or interfering with the furnace’s operation. To fix this issue, you’ll need to clear the clogged condensate line.
7. Fuel Supply Issues
A gas furnace requires a proper gas supply to function correctly. If there is a problem with the gas supply, either from the gas line or the furnace’s gas valve, the furnace may blow cold air and then shut down. In this case, it’s essential to call a professional HVAC technician to diagnose and resolve the issue.
8. Leaking Air Ducts
If your air ducts are leaking, cold air from your attic or other unconditioned spaces can mix with the warm air being circulated by your furnace. This can result in cold air blowing from your vents. To fix this issue, you’ll need to have your ducts inspected and sealed by a professional.
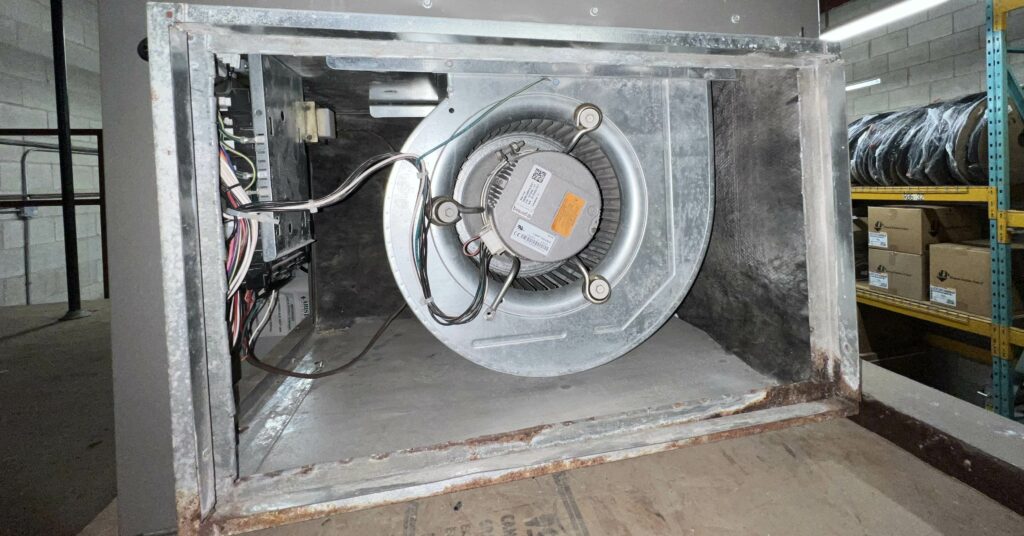
9. Damaged or Malfunctioning Components
Various components within your furnace can become damaged or malfunction, leading to cold air blowing from your vents. Some examples include the furnace blower motor, control board, and heat exchanger. If you suspect a damaged or malfunctioning component, it’s best to call a professional HVAC technician for a thorough inspection and repair.
10. Thermostat Wiring Issues
If your thermostat has been recently installed or replaced, it’s possible that there may be an issue with the wiring. Incorrect or faulty wiring can cause your furnace to blow cold air. In this case, it’s best to call a professional HVAC technician to inspect the wiring and ensure the thermostat is properly connected and compatible with your system.
Conclusion
A furnace blowing cold air can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience, but the good news is that many common issues can be resolved with some troubleshooting and simple DIY repairs. By understanding the potential causes and knowing when to call in a professional, you can quickly restore warmth and comfort to your home. Remember to maintain your furnace regularly, including changing the air filter and scheduling annual inspections, to prevent future issues and prolong the lifespan of your heating system.