Heat Pump vs Furnace: Which Should You Choose?
When it comes to heating your home, there are several options available to you. Two of the most popular options are heat pumps and furnaces. While both are effective at providing warmth to your home, they differ in several ways. In this article, we will discuss the differences between heat pumps and furnaces to help you determine which one is better for your home.
What is Heat Pump?
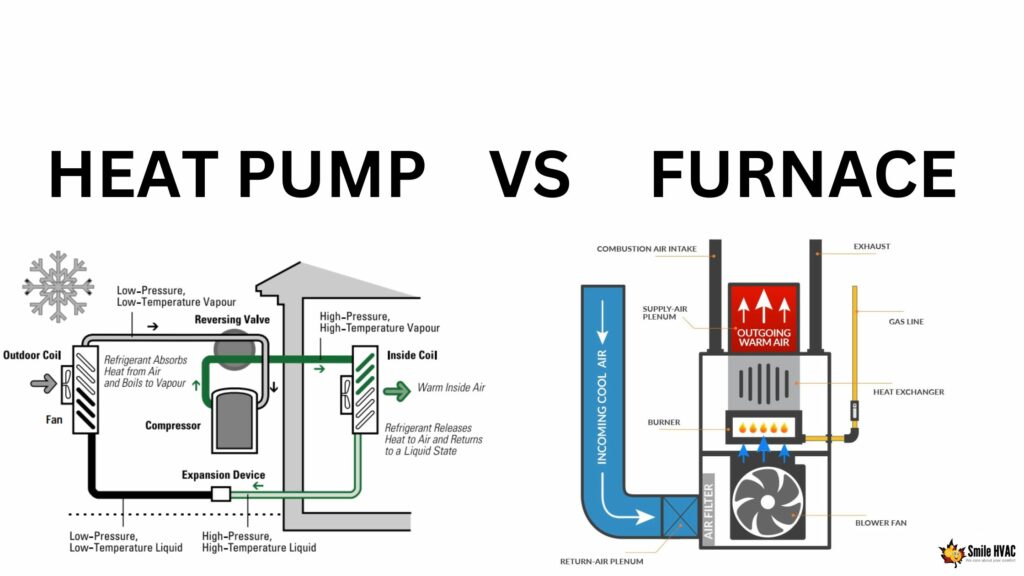
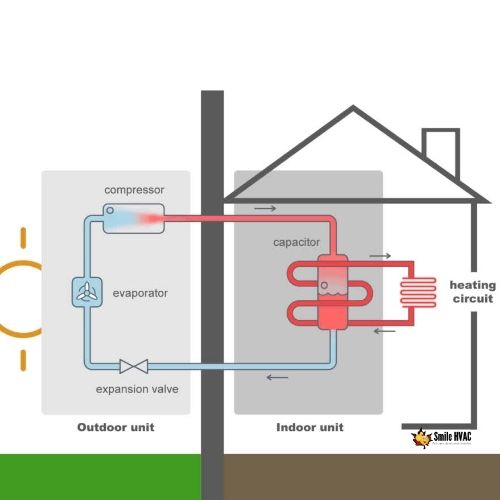
A heat pump is a heating and cooling system that uses electricity to move heat from one location to another. Heat pumps work by transferring heat from the outdoor air or ground to your home in the winter to provide heating, and by transferring heat from your home to the outdoors in the summer to provide cooling.
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
Heat pumps use refrigerant to absorb heat from the outdoor air or ground, and then transfer that heat indoors using a compressor and a heat exchanger. In the winter, the heat pump extracts heat from the outdoor air or ground and transfers it inside to warm your home. In the summer, the heat pump removes heat from inside your home and transfers it outside to keep your home cool.
Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient because they do not generate heat, but rather move heat from one location to another. They can provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile and efficient option for year-round home comfort. Additionally, some heat pumps can be used in conjunction with a furnace or other heating system to provide supplemental heating during extremely cold temperatures.
What is a Furnace?
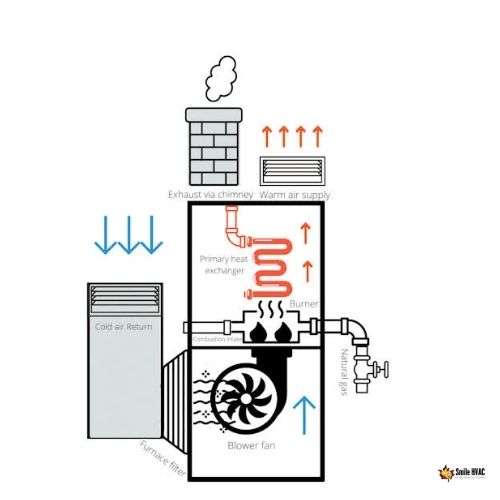
A furnace is a heating system that uses fuel (such as gas, oil, or electricity) to generate heat and distribute it throughout a home or building. Furnaces work by heating air and then blowing it through ductwork to deliver warm air to different rooms and areas.
How Does a Furnace Work?
Gas and oil furnaces use burners to heat air, while electric furnaces use heating elements to generate heat. The warm air produced by the furnace is distributed throughout the home or building using a network of ducts, vents, and registers.
Furnaces are a popular heating option because they can provide reliable and consistent heat, and can be used in a wide range of climates and home sizes. They can be fueled by a variety of energy sources, including natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity. However, furnaces can be less energy-efficient than some other heating options, such as heat pumps, and may produce emissions during operation.
Heat Pump vs Furnace
Heat pumps and furnaces are both commonly used to heat homes, but they differ in how they generate and distribute heat. Here are some of the main differences between heat pumps and furnaces.
- Heat Generation: Heat pumps move heat from one place to another using refrigerant, while furnaces generate heat through the combustion of fuel, such as natural gas or propane.
- Efficiency: Heat pumps are typically more energy-efficient than furnaces because they move heat instead of generating it. However, in extremely cold temperatures, a heat pump’s efficiency may decrease, while furnaces work well in cold weather.
- Cooling Functionality: Heat pumps can also provide cooling for your home during warmer months, whereas furnaces do not have this capability.
- Cost: Heat pumps are typically more expensive to install than furnaces, but they can provide cost savings on energy bills in the long run.
- Safety: Furnaces can pose a safety risk if not properly maintained, as they generate carbon monoxide and other gases that can be harmful if not properly vented. Heat pumps do not have this risk.
- Maintenance: Heat pumps require regular maintenance to keep them working efficiently, including changing air filters and cleaning the outdoor unit. Furnaces may require less frequent maintenance, but it is important to have them checked regularly for safety and efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Heat Pump
Heat Pump Pros
- Energy-efficient – Heat pumps move heat instead of generating it, making them more energy-efficient than furnaces.
- Dual-purpose – Heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile option for year-round home comfort.
- Environmentally friendly – Heat pumps produce fewer emissions than furnaces, which can be better for the environment.
- Low operating costs – Since heat pumps use less energy, they can result in lower operating costs over time.
Heat Pump Cons
- Initial cost – Heat pumps can be more expensive to install than furnaces, which can be a barrier for some homeowners.
- Performance in cold climates – Some heat pumps struggle to provide adequate heating in extremely cold temperatures.
- Potential for maintenance – Heat pumps have more components than furnaces, which may require more maintenance and repair.
Pros and Cons of Furnace
Furnace Pros
- Reliable – Furnaces can provide reliable and consistent heating, even in very cold temperatures.
- Wide range of fuels – Furnaces can be fueled by a variety of sources, including natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity.
- Lower initial cost – Furnaces are generally less expensive to install than heat pumps.
- Less maintenance – Furnaces have fewer components than heat pumps, which can mean less maintenance and repair over time.
Furnace Cons
- Energy efficiency – Furnaces can be less energy-efficient than heat pumps, which can result in higher operating costs over time.
- Emissions – Furnaces may produce emissions during operation, which can be harmful to the environment.
- Single purpose – Furnaces only provide heating, which may be a drawback for those looking for a dual-purpose system.
- Less environmentally friendly – Furnaces may not be as environmentally friendly as heat pumps due to their emissions.
OIL FURNACE VS HEAT PUMP
Oil furnaces and heat pumps are two different types of heating systems that differ in their technology and method of operation.
| S. No | Oil Furnace | Heat Pump |
| 1. | Oil furnaces burn oil to generate heat.
|
Heat pumps move heat from the air or ground using refrigerant. |
| 2. | Oil Furnaces are less energy-efficient than Heat pumps. The efficiency of an oil furnace is measured by its Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE), which is the ratio of the heat output to the fuel consumed. The higher the AFUE, the more efficient the furnace.
In extremely cold temperatures, oil furnaces can maintain their efficiency. |
Heat pumps are typically more energy-efficient than oil furnaces because they move heat instead of generating it. The efficiency of a heat pump is measured by its Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF), which is the ratio of the heat output to the electricity consumed. The higher the HSPF, the more efficient the heat pump.
In extremely cold temperatures, the efficiency of a heat pump may decrease. |
| 3. | Oil Furnaces are less expensive to install. | Heat pumps are generally more expensive to install than oil furnaces, but they can provide cost savings on energy bills in the long run.
|
| 4. | Oil furnaces do not have the capability to provide cooling for warmer months. | Heat pumps can also provide cooling for your home during warmer months |
| 5. | Oil furnaces can pose a safety risk if not properly maintained, as they generate carbon monoxide and other gases that can be harmful if not properly vented. | Heat pumps do not have this risk.
|
| 6. | Oil furnaces require the use of fossil fuels and contribute to air pollution. | Heat pumps use electricity and produce no direct emissions. |
| 7. | Oil furnaces require regular maintenance to ensure they are working safely and efficiently, including cleaning and changing the oil filter. | Heat pumps also require regular maintenance, such as cleaning the outdoor unit and changing the air filter.
|
ELECTRIC FURNACE VS HEAT PUMP
Electric furnaces and heat pumps are two common types of heating systems that use electricity to generate heat. Here are some of the main differences between electric furnaces and heat pumps.
| S. No | Electric Furnace | Heat Pump |
| 1. | Electric furnaces use heating elements to generate heat. | Heat pumps move heat from the air or ground using refrigerant. |
| 2. | Electric Furnace is less energy efficient.
However, electric furnaces can maintain their efficiency in extremely cold temperatures. |
Heat pumps are typically more energy-efficient than electric furnaces because they move heat instead of generating it.
However, in extremely cold temperatures, the efficiency of a heat pump may decrease.
|
| 3. | Electric furnace installation costs less compared to Heat pumps.
They can range from $1,500 to $3,500 or more, depending on the size of the furnace and the complexity of the installation. |
Heat pumps are typically more expensive to install than electric furnaces because they require more equipment and labor.
The cost of a heat pump installation can range from $4,000 to $10,000 or more, depending on the size of the system and the complexity of the installation. But they can provide cost savings on energy bills in the long run.
|
| 4. | Electric Furnace only provides heating and does not provide cooling. | Heat pumps can also provide cooling for your home during warmer months. |
| 5. | Electric furnaces do not produce emissions during operation. | Heat pumps use electricity and produce no direct emissions. However, the emissions associated with electricity generation can vary depending on the source of the electricity. |
| 6. | Electric furnaces require minimal maintenance. | Heat pumps require regular maintenance, such as cleaning the outdoor unit and changing the air filter. |
Which one is best for you?
The choice between a heat pump and a furnace depends on several factors, including your climate, energy costs, budget, and personal preferences.
Based on energy efficiency
Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient than furnaces because they move heat instead of generating it. This can result in cost savings on energy bills over time, particularly in moderate climates.
Heat pumps can also provide both heating and cooling, which can be convenient for year-round home comfort.
Based on the Climate
Heat pumps may not be the best choice in extremely cold climates, where they may struggle to provide adequate heating. Additionally, the initial cost of a heat pump installation may be higher than a furnace installation.
Furnaces, on the other hand, can provide reliable and consistent heat and can be used in a wide range of climates and home sizes. They can be fueled by a variety of energy sources, including natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity. Furnaces may be more suitable for very cold climates, where they can provide reliable and efficient heating.
Dual Fuel Heating systems
Dual fuel heating systems combine the energy-efficient heating capabilities of a heat pump with the reliable heating power of a furnace. This system is designed to automatically switch between the two heating sources, depending on the outdoor temperature, to provide the most efficient and cost-effective heating.
When the outdoor temperature is above a certain threshold, the heat pump will provide heating by extracting heat from the outdoor air and moving it inside. This is an energy-efficient method of heating, as it does not require the use of fuel to generate heat.
However, when the outdoor temperature drops below a certain threshold, the furnace will take over and provide heating using fuel, such as gas or oil. This ensures that the home stays warm and comfortable, even in extremely cold temperatures.
Dual fuel heating systems can be more expensive to install than single heating systems, but they can provide significant energy savings and cost savings on energy bills in the long run. Additionally, they can provide the reliability of a furnace with the energy efficiency of a heat pump, making them a popular choice in areas with fluctuating temperatures.
FAQ
What is the difference between a heat pump and a furnace?
A heat pump uses electricity to move heat from the outside air or ground into your home to heat it. A furnace, on the other hand, burns fuel (such as natural gas or oil) to create heat that is distributed throughout your home.
Which one is more energy-efficient heat pump or furnace?
Generally, a heat pump is more energy-efficient than a furnace, especially in moderate climates. This is because a heat pump only uses electricity to move and transfer heat, while a furnace must burn fuel to create heat. However, in colder climates, a furnace may be more efficient as it can produce more heat per unit of fuel burned.
Which one is more cost-effective heat pump or a furnace?
his depends on several factors, including your climate, energy prices, and the efficiency of the unit. In general, a heat pump may be more cost-effective in moderate climates with mild winters, while a furnace may be more cost-effective in colder climates with harsh winters.
Can a heat pump replace a furnace?
In moderate climates, a heat pump can often replace a furnace as the primary heating source. However, in colder climates, a furnace may still be needed as a backup or supplemental heating source.
How often do I need to maintain my heat pump or furnace?
Both a heat pump and a furnace require regular maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently and safely. It is recommended to have your unit serviced by a professional once a year.